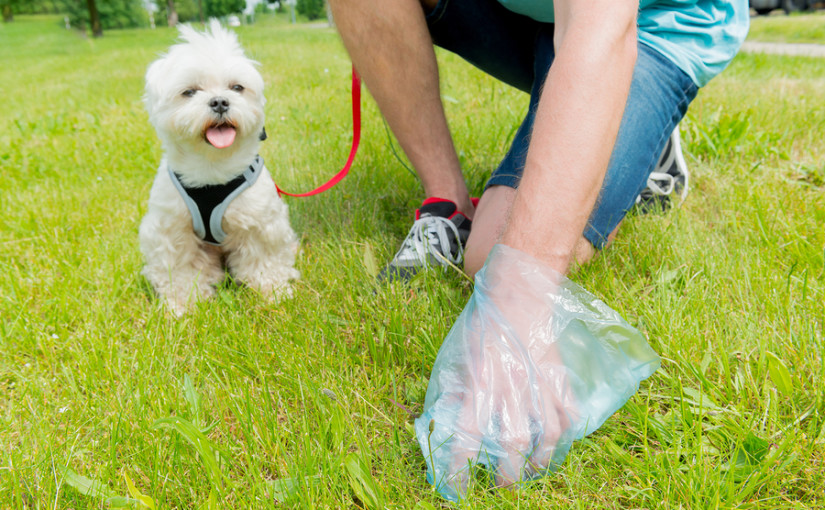
The Big Scoop campaign has kicked off this week; organised by Dog’s Trust and Keep Britain Tidy, this campaign aims to highlight how easy it is to scoop your dog’s poop, and appeals to dog owners to do just that. The Big Scoop will support local councils, and educate dog owners. A survey conducted recently in Cardiff showed that the general public dislike dog mess more than general litter or people smoking in public, making dog poo the nation’s biggest bugbear.
The UK is home to over 8 million canines, who produce over 1000 tonnes of waste between them every day – that weighs as much as 200 double-decker buses! Of course, this wouldn’t be a problem if all of the mess was scooped up, but this is sadly far from the truth.
Alex Jackson, who is Head of Campaigns at Dogs Trust, says:
“Dog poo is still one of the biggest complaints received by local councils every year, with 81,000 complaints received from members of the public last year alone, so it’s important that everyone is aware of how simple disposing of dog mess can be.”
Owners who don’t scoop their dog’s poop are breaking the law, and face an £80 fine if caught. The problem is ‘if caught’; many irresponsible dog owners who don’t scoop, commit the act when nobody is about, or by cover of darkness, knowing they will get away with it.
But why do we dislike dog poo so much? And why should we clear it up straight away from our streets, paths, and parks? We explore the reasons below.
Continue reading Dog mess: the nation’s most hated & dangerous litter